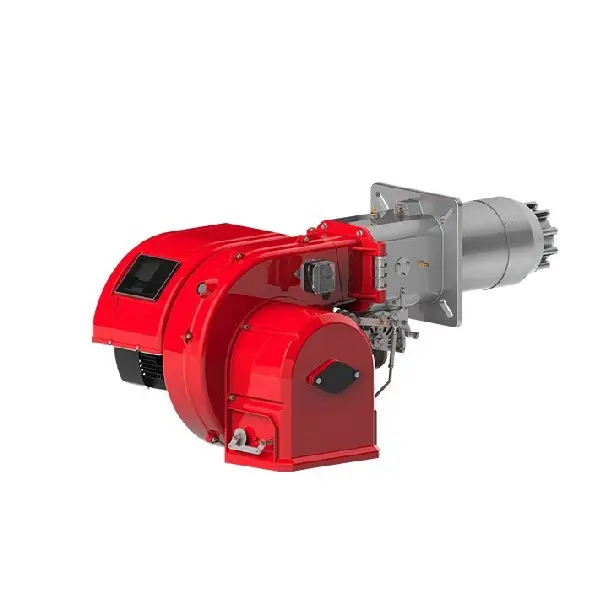
Introdução
UMA boiler burner is the part of a hot water or steam boiler that burns the fuel. Most boilers are either all-gas or all-oil. The gas and oil burners are designed to suit the type of boiler and application, so it’s important to select one that matches your needs as closely as possible.
How many types of boiler burners are there?
Oil boiler burners can be divided into two categories: hot-surface and forced. Hot-surface burners are the traditional type of burner that has been used for decades. They consist of a flame heating up a tube mounted on an electric or gas valve. When used with oil, these types of burners are efficient and work well but may require frequent cleaning as they can get clogged with soot over time. The forced-air burner is relatively new in comparison to its counterpart; it uses air pressure to push more oxygen into the firebox, increasing efficiency and reducing emissions by up to 90%. A pilot light will ignite when electricity is applied to the unit via a thermostat switch; this allows users to control their boilers manually or automatically depending on what settings you choose (por exemplo., auto vs manual).
Gas boilers use gas instead of liquid fuel like oil does so keep this in mind when choosing which type best suits your needs!
What are the different types of burners?
There are five main types of boiler burners: gas burners, oil burners, coal burners, biomass burners and diesel burners.
Gas burner: The combustion chamber is lined with refractory bricks or tiles and the power of the flame itself helps to dissipate any heat that might be too much for the tubes or flue pipes. Gas boilers are often seen in domestic applications because they have a very high efficiency rate; however they do have some disadvantages such as being expensive if you run out of gas during peak winter months when demand for heating is at its highest.
Clique aqui para obter sua cotação
What are burners on a boiler?
Boilers are used to produce steam and hot water. The fuel (carvão, óleo, gás natural, wood pellets or other biomass) is burned in the firebox of a boiler. The heat from this burning process heats up the water inside the boiler and produces steam.
Burners are used to heat water in boilers. They also can be used to heat air or oil for industrial processes such as drying grain or making carbon black.
What are the three classifications of burners?
A boiler burner is a device that heats up water or air to create steam. The three types of burners are gas, óleo, and coal.
- Gas burners use natural gas or propane to heat the water. They are very efficient and cost-effective because they don’t require extra fuel to ignite the combustion process, unlike oil and coal boilers. No entanto, they can be dangerous if not used properly; if there is an ignition source nearby, it could lead to an explosion!
- Oil burners use fuel oil as their heating source—this type of burner is commonly used in industrial settings because of its high-power output and efficiency at different temperatures. The downside? It’s expensive compared with other types; plus you have less control over temperature than with gas or coal boilers because it works on a fixed schedule rather than being manually adjusted by hand (like with other types). If there’s an accident during operation due to improper maintenance procedures like clogged lines or broken pumps (which cause excessive pressure buildups), then this could lead directly into disaster scenarios such as explosions!
- Coal-fired boilers operate similarly with oil-fired ones except their primary difference lies in how long each takes before reaching full capacity after starting up for first time–while oil takes about two weeks before reaching full capacity level after being turned off previously due mainly due lack access information needed before starting up again vs coal which only takes one day only
What is the most common type of burner?
If you’re looking for the most common type of burner, it’s the gas burner. Gas burners are used for residential and commercial boilers because they require less maintenance than other types of burners. Oil-fired boilers are also common because oil is easy to store and transport, unlike coal or wood fuels. Coal-fired boilers are typically used when there isn’t access to natural gas lines or if a facility needs lots of heat from a small amount of space.
The four main types of burners include:
- Gás (GLP) Boilers
Gás (GLP) boilers use natural gas stored in tanks to heat water or steam that drives generators with electricity instead of burning fuel directly like in coal-, oil-, or wood-burning boilers
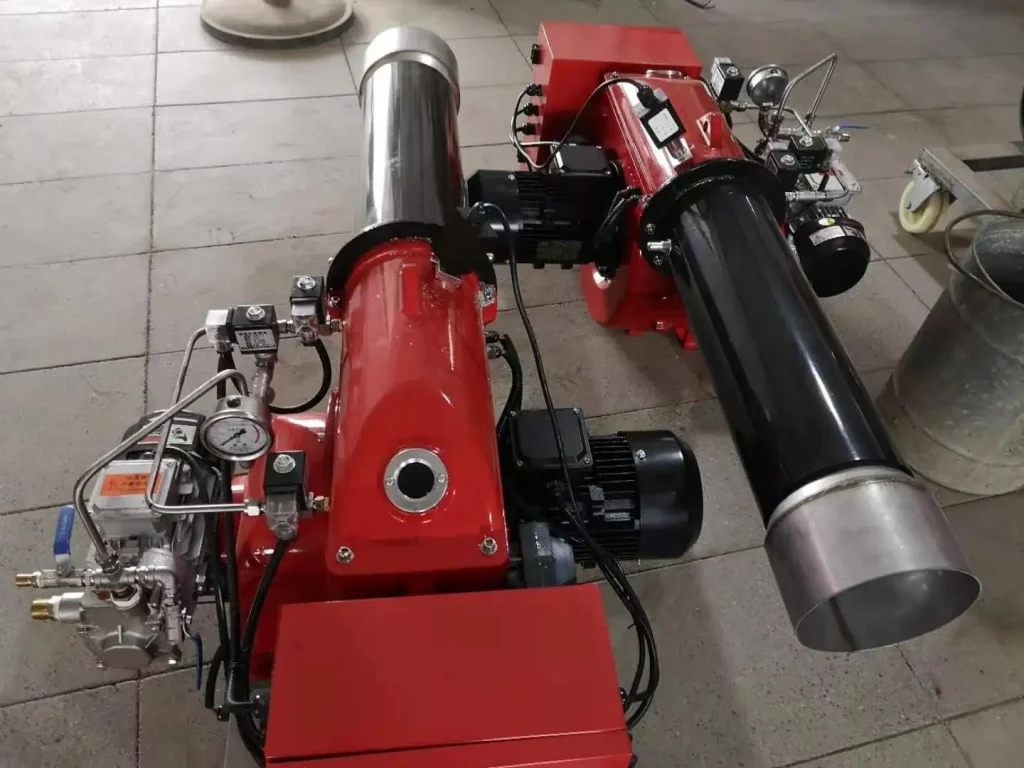

boiler burner
How do I choose a boiler burner?
When choosing a boiler burner, you must consider several factors.
- Is the burner compatible with your boiler? Some burners are designed for specific types of boilers. If you have an oil-fired steam boiler, por exemplo, you’ll need to get an oil-fired steam boiler burner.
- Is the burner compatible with your fuel type? You should always choose a fuel type that’s right for your home or business. Por exemplo, if you’re planning on burning wood as a heat source (which is viable in some areas), then it’s important to purchase a wood-burning appliance such as ours and not one intended for burning coal or propane instead!
- Does it fit into your current delivery system? Don’t forget about this step either—you don’t want to buy something and then realize later on that there’s no way it will work because there isn’t enough room behind where they were installed before they were put into place during construction activities taking place outside their doors during their opening hours between 8 AM – 6 PM Monday through Friday except holidays when hours may vary depending upon location so call first if unsure about what kind
How do I choose a boiler burner?
Choosing the right boiler burner is a matter of matching your needs to the requirements of the different types of boilers. The following are some factors you should consider when choosing a burner for your application:
- Which type of fuel will power it?
- How much fuel do I need to use?
- How much heat do I need from my boiler?
What are burners used for?
Burners are used to heat water. In boilers, they are used to heat water that is then turned into steam.
What is diesel burner?
Diesel burners are used for small boilers that have a low demand, such as those found in private residences. This type of boiler burner burns diesel oil or kerosene, and is also known as a diesel stove.
oil fired boiler burner
Oil fired boiler burners are used to heat water in boilers. When steam is generated, it goes into the turbines which produce power. The hot vapor enters the condenser where it is cooled and condensed back into liquid form. This process creates electricity.
gas boiler burner
Gas boiler burners, or gas boilers as they are commonly known, are the most common and popular type of heating systems in use today. They’re also the most efficient, environmentally friendly, versatile and overall best option when it comes to boiler burners. However this means that they’re also more expensive than other types of burner systems.
Gas boiler burners have been around for many years now but several technological advancements have resulted in more efficient designs being produced which have helped them become even more popular as a reliable source of heat for homes and businesses alike.
coal burner
A coal burner is a type of boiler that burns coal as its fuel source. Coal burners are useful for providing heat to homes and businesses, like many other types of boilers. The difference between a coal burner and other types of boilers is that the former requires coal to be burned inside it in order for it to work properly, whereas some other types can use different types of fuels and still operate properly. A typical example would be natural gas-powered boilers, which do not need any special kind of fuel outside what they already have stored inside them at any given time (usually natural gas).
While there are many different kinds of burners available on the market today (such as oil-fired or electric), this article will focus primarily on those meant specifically for burning coal as their energy source: namely those known colloquially as “coal fired” units.”
Takeaway:
The type of boiler burner you choose depends on the process you need to heat. Por exemplo, you may use a steam boiler to heat water in your home or office. In other situations, for example when dealing with industrial heating applications, you might need an air-heating boiler or an oil-burning boiler.
The type of fuel used also comes into play when choosing a burner for your setup. You can use coal-burning boilers for large industrial facilities requiring large amounts of energy; no entanto, these types of boilers are usually only found at power plants due to their high cost and environmental impact. A better option is diesel fuel or natural gas combustion units such as those offered by Burner World USA Incorporated (Burner World USA) because they’re much cheaper than coal while being cleaner and less expensive than electricity-powered systems like electric boilers or gas turbines (which require significant maintenance).
Conclusão
There are four main types of boiler burners: premix, potência, industrial and gas burners. Premix burners offer the most precise control over the air and fuel mixture entering a burner chamber. Power burners are used in larger boilers for commercial applications such as heating water or warming air in a building. Industrial boilers typically use power or industrial burners. Oil-fired boilers may use premix or power burners, but both types have been phased out of production due to environmental concerns about using fossil fuels.


